Solvency statistics
The Financial Supervisory Authority publishes quarterly information on the solvency of private-sector pension providers. Based on this information, we update our own solvency statistics for pension insurance companies as well as for company pension funds and industry-wide pension funds. On the basis of financial statements, we also compile time series charts on the development of solvency in pension insurance companies.
Content of this page
Development of the solvency ratio and position

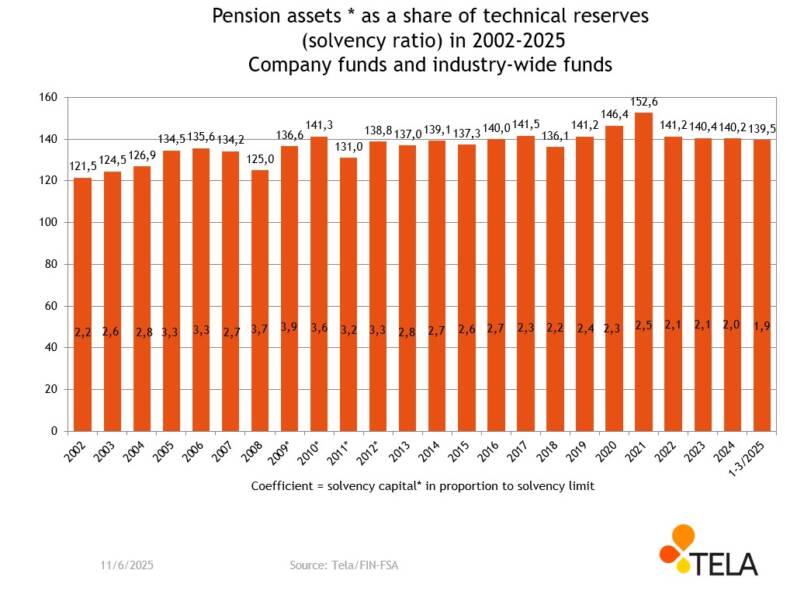
* The method of calculating the solvency ratio has changed over time. Before 2013, the solvency ratio was calculated by dividing the working capital by technical provisions. In 2013–2016, the solvency ratio was calculated by dividing the solvency capital by technical provisions. As of 2017, the solvency ratio has been calculated by dividing pension assets by technical provisions.
In the time series of the figures, the data prior to the year 2017 have also been expressed using the current calculation method.
The figures show both the solvency ratio of pension providers, i.e. the ratio between the pension assets managed by the operator and the technical provisions (columns), and the solvency position, which describes the amount of the solvency capital in relation to the solvency limit (coefficient).
The most significant downturn in the solvency ratio occurred in 2008, when the global financial crisis had its strongest impact on pension assets. The sharp decline in the net asset value of investments also led to a reduction in the market value of earnings-related pension assets. To avert the situation where pension providers’ investment assets would have had to be sold at a loss in order to reduce risks and increase solvency, the provisions on investment activities and solvency were temporarily amended. Thus, pension providers’ solvency was supported in 2008 by a transfer from the liquidity buffer of non-funded pensions, i.e. from the provision for pooled claims. The transfer was in use until the end of 2012.
Time series for solvency at each pension insurance company
Below, based on financial statements, we have compiled company-specific time series charts associated with the solvency of pension insurance companies. We update the charts annually in June after the the previous year’s certified financial statements have been released.
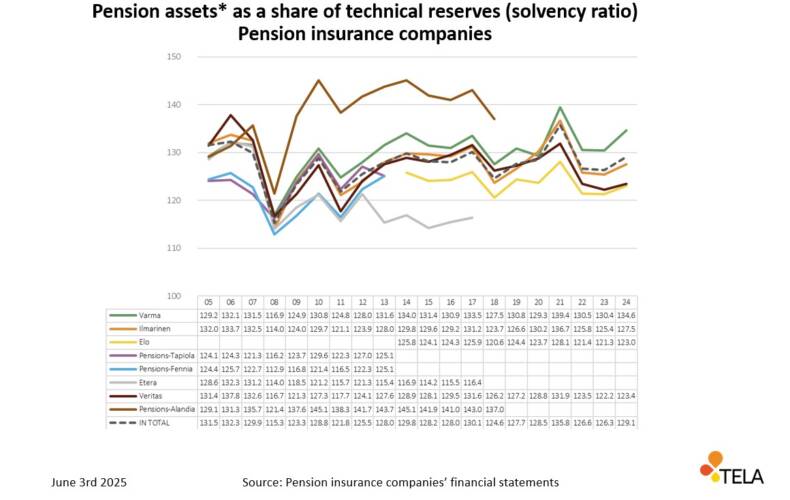
* The method of calculating the solvency ratio has changed over time. Before 2013, the solvency ratio was calculated by dividing the working capital by technical provisions. In 2013–2016, the solvency ratio was calculated by dividing the solvency capital by technical provisions. As of 2017, the solvency ratio has been calculated by dividing pension assets by technical provisions.
In the figure, the data prior to the year 2017 have also been expressed using the current calculation method.
The figure above describes the various operators’ solvency ratio for each pension insurance company, i.e. the ratio of pension assets to technical provisions from 2005 onwards. This figure also shows the impact of the global financial crises in 2008 and 2011. In addition, the investment market experienced an unusually strong downturn in share prices in 2018, which is reflected as a downswing in the solvency ratio.
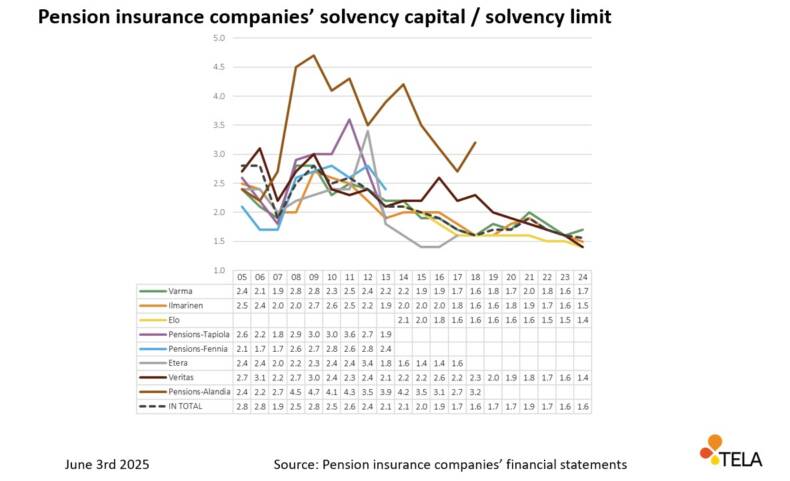
The second figure shows the solvency position of pension insurance companies, i.e. the ratio of solvency capital to the solvency limit. The impact of the financial crisis of 2008 and the consequent temporary law passed can also be seen in this time series .
Time series as a PDF file
The time series graphs can also be downloaded as the attached PDF file:


